

- RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER HOW TO
- RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER SERIAL
- RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER DRIVER
- RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER FULL
You can use the code below to test the circuit and also complete the first project. > Learn more about How Easy Is It To Learn Arduino here.Ĥ) Arduino Program to create a simple Melody using Piezo buzzer The above buzzer can work from 3V to 24 V hence this is a good choice. Quick Tip: Buy the Buzzers, which are compatible with Arduino UNO.
RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER SERIAL
What is the purpose of noTone() function?Ĭomponents Needed To Use Arduino Serial Plotter Hardware Components.

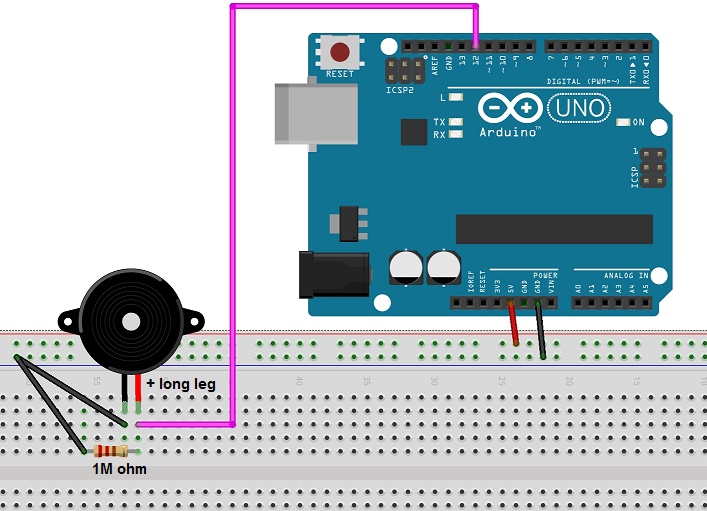
How do you connect the buzzer to Arduino Mega?.How do you turn off the buzzer in Arduino?.How do you turn on the buzzer in Arduino?.3) Arduino Simulation of three buzzer example.2) Program to drive three buzzers using Arduino.1) Connect three buzzers to Arduino UNO.
RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER HOW TO
RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER DRIVER
There should be a decoupling capacitor next to the driver transistors, which isn't shown. The output power will be around 400mW, thanks to the voltage drop of the emitter followers, which should be loud enough. To drive a 0.5W 8Ohm speaker from an Arduinp I'd recommend using a pair of emitter followers and an AC coupling capacitor. Using one squarewave source and an AC coupling capacitor would reduce the power to half again, at 0.78125W, but the sound output would not change, since the DC component will be blocked. If only one square wave source were used, with the other end of R1 connected to 0V, the power would halve to 1.5625W, but there would be 2.5V of DC across it, which would do nothing but heat the voice coil, if it were a speaker. The RMS current through the 8Ohm resistor is 625mA and the power dissipated 3.125W. V1 and V2 represent differential outputs. That's true, but is completely irrelevant here, as the original poster is talking about driving a load from an MCU output pin, not a linear amplifier, be it class AB or D.
On the other hand you can drive a speaker with a single transistor if you don't mind something crude. pull-up and pull-down) otherwise all you'll hear is the first tick. It's also good to bear in mind that piezos are capacitive, so they don't provide a DC path so it's essential to be able to drive it in both directions (i.e. drive the two ends of the speaker in opposite directions). However with an 8-ohm speaker you could get a reasonable amount of power from a 5v supply, especially if you run it in bridge mode (i.e. A while back I added an alarm sounder to a PCB and ran an H-bridge from a 24v supply to get max output.
RESISTANCE OF ARDUINO PIEZO BUZZER FULL
You may also find that you need a lot of voltage to get full power. Piezos are typically very dependent on being mounted correctly (glueing to a metal surface or PCB is often seen) and if you hold one in free space there will be very little output. more sound output per Watt input, but if you go away from resonance, even by tens of Hz, you'll get much less. If you drive a piezo at close to its resonant frequency, which is often in the 2 to 8kHz range, you can get higher sensitivity, i.e. Now 80dB is quite loud, noisy indeed, but 1W is also a fair bit of power to deliver (although sound systems often claim to be capable of hundreds of watts, this is unrealistic in normal operation). (Magnetic) loudspeaker sensitivity is generally quoted in dBA per Watt, often at 1m from the speaker.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
